|
Insight into and Impact of Abu Dhabi
Municipality on Abu Dhabi City: An
Interview with Abdulaziz Al Kindi,
Senior Contract Manager

Sasha Hodgson (1)
Hamad Al Neyadi (2)
Mohamed Al Jabri (2)
(1) Dr. Sasha Hodgson, Assistant
Professor, Zayed University, Abu Dhabi,
United Arab Emirates
(2) Graduate student, Zayed University,
Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Correspondence:
Dr. Sasha Hodgson, Assistant Professor
Zayed University,
P.O. Box 144534
Abu Dhabi
United Arab Emirates
Email: Sasha.Hodgson@zu.ac.ae

Abstract
Abu Dhabi Municipality was established
in order to develop the infrastructure
of the city of Abu Dhabi and turn
it into a modern city. Abu Dhabi Municipality
has several sectors and each sector
is in charge of numerous projects
and activities. Through an interview
with Abdulaziz Al Kindi, we gain a
unique insight into the municipality,
it's structure and impact on Abu Dhabi
City such as environmental awareness,
creation and renewal of urban structures,
transportation, road safety, demolition
of illegal accommodation, agriculture
control, and improving housing projects.
The report provides a worthy blueprint
for other regional municipalities
installing systems and structures.

Introduction
Abu Dhabi Municipality emerged as
the Department of Abu Dhabi Municipality
and Town Planning in 1962. The vision
of Abu Dhabi Municipality is to provide
modern infrastructure and outstanding
municipal services for a promising
capital (2011). Abu Dhabi is the U.A.E
capital city. It is a common misconception
that Dubai is the capital however,
with Abu Dhabi Investment Authority
currently ranked the No 1 Sovereign
Wealth Fund in the world, it is clear
where the wealth really is, in Abu
Dhabi.
Through a unique interview with Abdulaziz
Al Kindi, a Senior Contract Manager,
we gain insights into the current
structure of the organization in addition
to the true impact of the municipality
on the capital city.
Organizational Chart of Abu Dhabi
Municipality
Abu Dhabi Municipality emerged as
the Department of Abu Dhabi Municipality
and Town Planning in the 1962. The
first municipal board for Abu (?Dhabi)
City was appointed in 1969 under the
royal decree and 'Al Sunni Banga'
was appointed as the first manager.
The board was charged with the responsibility
of offering comprehensive services
to the public and ensuring proper
planning and development of Abu Dhabi
City, with maintenance services, regularized
road networks, lighting works, sewerage,
establishing public markets in different
areas and launching of the Agriculture
Development Plan. Since its inception,
the Abu Dhabi Municipality has devised
major objectives, including various
projects' implementation targeted
at developing modern city infrastructure
such as road networks, drainage systems,
and modern means of transportation,
bridges, and development project consolidation.
In addition, the municipality has
been increasingly moving towards achieving
the goals stipulated in the development
plans. The priority of Abu Dhabi Municipality
is to establish a suitable living
environment for the residents of the
Abu Dhabi City by establishing modern
amenities (Department of Municipal
Affairs, 2013).
Vision
The vision of Abu Dhabi Municipality
is to provide modern infrastructure
and outstanding municipal services
for a promising capital (Abu Dhabi
City Municipality, 2011).
Mission Statement
The mission of Abu Dhabi Municipality
is to provide the residents of Abu
Dhabi City with a healthy, quality
living environment through innovative
planning, improved infrastructure,
and enhanced municipal services (Abu
Dhabi City Municipality, 2011).
Sectors of Abu Dhabi
Municipality
Municipal Infrastructure &
Asset Sector

The municipal infrastructure and
asset sector consists of three major
divisions, including the parks and
recreation facilities division, municipal
roads and infrastructure division,
and the infrastructure and services
coordination division.
Functions of the Municipal Infrastructure
and Assets Sector
• To plan the development and
prosperity of Abu Dhabi City to be
one of the top five global capitals
that provides the highest standard
of quality services.
• To maintain operation, safety,
and service levels to ensure that
approximately eighty-five percent
of the road network in the city meets
the global standards that have been
set for scale service roads.
• To achieve equilibrium between
infrastructure and greenery to keep
up with the growing population density
by augmenting the rate of green area
per capita.
• To prepare controls and programs
to acknowledge, develop operations,
and maintain management projects.
• To develop and train national
staff in the arena of operation, design,
implementation, and maintenance.
• To adopt current technological
science in irrigation and agriculture
to minimize maintenance and operating
costs, and to optimize water and minimize
environmental degradation.
• To institute a database for
road asset management to predict future
service needs and maintenance requirements,
thereby reducing public expenditure.
The functions of the Municipal Roads
and Infrastructure Division include:
• To prepare a consolidated budget
and master plan of infrastructure
and road projects.
• To maintain local road networks
to a level that meets the highest
excellent standards and quality.
• To ensure the highest levels
of road safety for all road network
users.
• To recommend new projects that
can improve roads and bridges network
performance, to conduct primary studies
as well as economic feasibility and
technical studies, and to follow up
improvement and development projects
undertaken by service providers.
• To prequalify consultants and
contractors to authenticate their
competencies with regard to accomplishing
various projects, and to endorse supervisory
personnel and staff at site
• To organize reference terms
to invite the participation of consultants
in new projects, obtain the necessary
approvals, and to bring together the
list of consultants to be invited.
• To review and audit design
plans and reports that consultants
submit during the successive design
phases, that is, initial, primary,
and final, from all the perspectives
of engineering, including materials,
roads, traffic, sewage, traffic, and
lighting.
• To follow up with consultants
and contractors at construction and
maintenance stage to ensure that there
is conformity between contracts and
projects, and to prepare periodical
reports about projects being studied
as well as the statistics needed by
senior bodies.
• To manage maintenance and operation
contracts of traffic systems and light
signals in Abu Dhabi City.
• To supervise the removal and
demolition of visible aspects that
disfigure the general appearance of
Abu Dhabi City
Process of a new project:
Abdulaziz Al Kindi explained how new
projects are set in motion. According
to his answers, the process is explained
below:
There are three main parties involved
in the process of a new project:
1. Clients
2. Consultants
3. Contractors
Abdulaziz explained that they must
first generate an idea of the project
and identify the required budget.
He illustrated that every department
proposes a budget to the main management,
which is a committee who then proposes
to the Executive Council. The proposals
are then studied and determined before
providing the funds.
After that comes the tendering process,
which is finding a consultant to work
on the design of the project and to
supervise the operations performed
through the project. With the tendering
process, the client tries to find
the best consultant with the lowest
price and the best design.
After choosing the lowest bidder from
the consultants, the chosen one must
finish the final design needed for
the project, then prepare all contractual
documents needed for the contractor.
After the final design and the tender
documents are done, they will be used
to ask for contract bidders who present
their technical and financial reviews,
which will then be revised and scored
to find the best bidder. After the
contractor is chosen, the contract
will be signed between the client
and the contractor allowing him to
start working on the project.
The consultant is also responsible
for estimating the cost of the project
and to supervise the operations done
by the contractor. However, not all
contracts indicate that the consultant
who designs the project does the supervision;
there are some contracts that hire
one consultant to design the project
and another one to supervise the operations.
Support Services Sector
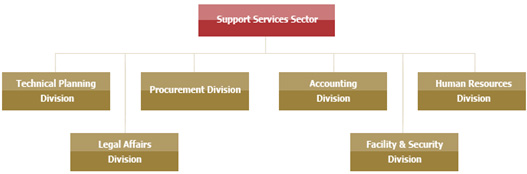
The functions of this sector include
the following:
• Devising strategies to provide
all the required services to the municipality
• Supervising quality and performance
across the various divisions of the
sector
The divisions of this sector include
accounting, technical planning, legal
affairs, facility and security, human
resources, and procurement divisions.
The functions of the procurement division
include:
• Conducting tender contracting
and limited methods of procurement
together with other projects within
the municipality
• Organizing procurement processes
for all affairs in the municipality
• Coordinating procurement activities
within the division
• Checking specifications of
purchased items
• Gathering information about
specific items, maintain suppliers'
list, and establish strong relations
among them to seek appropriate quotations.
• Negotiating with suppliers
and contractors after committee approval
• Studying and analyzing purchased
items based on price, quality, and
terms of delivery to ensure coordination
within the division.
• Receiving applications from
various divisions, studying them,
and providing all information and
data regarding suppliers and materials.
• Issuing purchase contracts
and orders
• Supervising and updating contractor
and supplier list
• Setting up the annual plan
for procurement
The procurement division provides
several services, including supplier
registration with ADM, rice purchase
from ADM, rice distribution cards,
tenders participation, and selling
of disposable materials through tenders.
General Manager Division
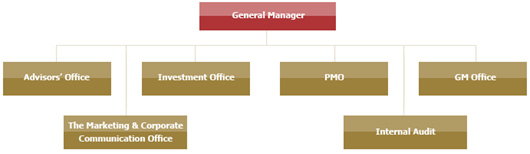
General Manager Offices are as follows:
1. Investment Office
2. General Manager Office
3. The Marketing and Corporate
Communication Office
4. Project Management Office
5. Internal Audit Office
6. Advisors Office
The general manager's office performs
the following functions:
• Directing development of long-term
and short-term plans, policies, and
objectives
• Ensuring effective implementation
of the municipality's mission and
vision
• Coordinating the alignment
of the work of various sectors with
set objectives, policies, and goals
• Monitoring the performance
of financial and strategic plans based
on established objectives and ensuring
that there is identification and implementation
of action plans as appropriate
• Directing as appropriate to
ensure that outputs and results are
achieved based on the operating budget
• Ensuring that there is proper
planning and delivery of municipal
services to all citizens
• Coordinating the development
and maintenance of infrastructure
and assets of the municipality, as
well as proper planning within the
municipality
• Representing the municipality
in all executive level meetings as
well as external organizations and
departments
The Municipal Services Sector
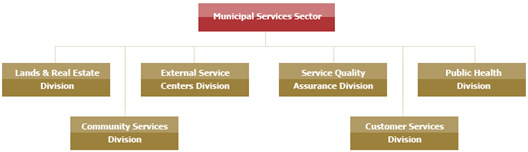
The Municipal Services sector consists
of the following divisions:
1. Community Services Division
2. Customer Services Division
3. External Service Centers
Division
4. Public Health Division
5. Lands & Real Estate
Division
The functions of the municipal services
sector include the following:
• Supervising property and land
management, including allocation and
registration
• Supervising high service level
activation to ensure successful community
services
• Leading the establishment of
comprehensive services centres by
providing integrated municipal government
services
• Using indirect service channels
to supervise service provision
• Supervising quality control
programs in services
Strategic Planning and Performance
Management Sector
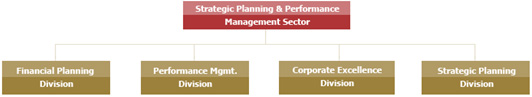
The Strategic Planning and Performance
Management sector is composed of the
following divisions:
1. Corporate Excellence Division
2. Financial Planning Division
3. Strategic Planning Division
4. Performance Management Division
The functions of the planning and
performance management sector include
the following:
• Developing the municipality's
strategic objectives
• Overseeing the development
of the five year strategic plan and
detailed annual plan of the municipality
• Overseeing the municipality's
development and formulation of financial
projections and plans
• Improving policies, procedures,
and implementation mechanisms as well
as development frameworks within the
municipality through supervision
• Supervising communication plans
and public relations within the municipality
Town Planning Sector

The Town Planning sector consists
of the following divisions:
1. Spatial Data Division
2. Urban Planning Division
3. Construction Permits Division
The town planning sector performs
the following functions:
• Detailed planning, managing
processes, division of urban uses,
and issuance of relevant rules and
policies
• Managing spatial data establishment,
distribution, updating, and maintenance
• Issuing building permits
• Managing segments and paths
of various service lines
Recently Completed Projects
The following completed projects are
stated in Abu Dhabi Municipality's
websites:
1. Al Mafraq Multi-Layer Interchange
Project
The project is vital in Al Mafraq
area and Abu Dhabi.

This bridge made a huge difference
in Al Mafraq area. This singular intersection
will be replaced with a multi-layer
intersection to make the traffic flow
smoothly. Abu Dhabi police estimated
that 24 thousand vehicles pass by
every hour. The project costs about
830 million DHS. According to engineer
Abdullah Al Shamsi, Acting Executive
Director of Municipal Infrastructure
and Assets Sector: "The Project
comes in the context of the Municipality's
multiple contributions and pioneering
projects to develop the city in keeping
with the economic & social drive,
improve the quality of services in
the capital and renovate roads and
infrastructure sector."
2. GPS Reference Station Network
Project
Geographical data reference

The geographical data reference provides
the Abu Dhabi Municipality with accurate
data that will help them develop the
Emirate of Abu Dhabi. Municipality
of Abu Dhabi City, Dubai Municipality,
Al Ain Municipality and Western Region
worked hard to complete this project
as early as possible to start working
with it and make use of it to develop
the UAE. This project took eight months
to be completed and is now operational.
3. Electronic building permits
system

The main purpose of the new Building
Permits e-System is to save hours
of valuable time waiting in queues.
It also saves the effort of the client
to wait for a long period of time
to complete paperwork. Creating a
username and a password and logging
in can allow you to use the electronic
building permit system. While the
client is logged in they will be eligible
to use it and the municipality will
handle the rest after they receive
the order of the client.
4. Sheikh Zayed Bin Sultan Al Nahyan
Mosque

It is one of the valuable landmarks
in Abu Dhabi. This mosque was funded
by His Highness Sheikh Zayed Bin Sultan
Al Nahyan, may he rest in peace. The
mosque has broken a lot of records
with their hand made carpet, dome
and chandelier in both diameter and
height. It is one of the symbols that
the UAE is famous for.
5. Sheikh Zayed Bridge (3rd Crossing)

The bridge was created by Zaha Hadid
and was designed in a remarkable way,
featuring creative artistic methods.
It is expected that this bridge has
a lifespan of not less than 120 years
and it handles wind speed of 160 KM/h.
Current Projects
Abdulaziz describes the current projects,
listed below:
1. Mohammed Bin Zayed City Project
Mohamed Bin Zayed City is one of the
emerging cities that Abu Dhabi Municipality
is willing to complete. Abu Dhabi
Municipality has a vision to build
a city that is completely different
from standard living. To reach their
goal in making this city achieve most
prestigious services and the best
living standard, the city will include
a number of iconic and tremendous
residence buildings. The city will
be holding 349 gigantic residential
towers. While the city holds approximately
5.8 million square meters, it is expected
to hold nearly 85,000 population.
Mohamed Bin Zayed city will be one
of the social aspects that the municipality
is willing to complete. The city will
allow its inhabitants to have a royal
lifestyle with the best services that
they can find. Adding to that the
city will hold a very promising and
remarkable working environment.

2. Sheikh Zayed Street & Tunnel
Sheikh Zayed street & tunnel will
be developed to make the traffic flow
in a very easy way thanks to the vital
structure and the artery of traffic
movement. Sheikh Zayed Street &
tunnel will help Abu Dhabi city to
provide to the people a very high
quality of transportation services.
To complete the project and achieve
it, three government departments:
Municipality of Abu Dhabi City, Abu
Dhabi Urban Planning Council and Department
of Transport worked together.

3. Data Base Enhancement Project
Data base enhancement is a vital project
that the Abu Dhabi Municipality are
willing to complete in a very well
planned agenda. This project will
provide a massive amount ofvaluable
data to the Abu Dhabi Municipality
database that will help them enhance
future development of Abu Dhabi city.
To control the information database
of all the regions that are controlled
by the Abu Dhabi Municipality, it
is necessary to extend the Abu Dhabi
Municipality geographic information,
which is what this project aims for.
This project will be huge in supporting
every future project and development
in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi.

4. Road Maintenance Projects (Ongoing)
a) Mainland
a. Area 1, 2 and 3: Yas, Mohamed
bin Zayed, KCA, KCB, Musaffah Industrial,
Musaffah Commercial, Bain Al Jesrain,
Officers City, etc..
b. Area 4, 5 and 6: Shahama,
Wathba, Baniyas, Al Rahba, Al Falah,
Shamkha, Shawamekh etc..
b) Island
a. All areas
Overall Responsibilities of Abu
Dhabi Municipality
According to Rafi (2013), Abu Dhabi
municipality performs the following
responsibilities:
ø Land Identification
Under this role, the municipality
is responsible for documenting and
recording territory allocated public
housing, residential land, commercial
land, industrial land, public utility,
agricultural land, and land trade
following adoption.
ø Land and Real Estate Transactions
Under this role, the municipality
is responsible for buying, selling,
and recording based on court ruling,
temporarily customizing the territory,
decoding booking land, recording booking
land, recording booking owner, recording
irreversible and donations, decoding
booking owner, and recording inheritance
and estates. It is also responsible
for registering industrial land, recording
leases, recording purchases and sales,
registering and redeeming mortgages,
modifying mortgage data, changing
mortgage value, withdrawal of land,
and commanding records.
ø Public Services
Under this role, the municipality
is responsible for certificate property
and ownership coupon, land housing
waiver, completing transaction during
the transition from employee to customer
site, ordering a copy of real estate
and land documents, and modifying
ownership data or name. It is also
responsible for certifying scheme
site, certificate search, property
valuation certificate, community services,
book parks visits, book and visit
beach, booking visit venues, and servicing
community and sports activities, public
health, servicing morgue, and servicing
recreational and cultural activities.
In addition, it is responsible for
setting a diseased body for burial,
transferring the deceased from the
morgue to the cemetery, providing
supervision, and guidance during burials,
and supervising matters of security
in the cemetery.
ø Certificates of Veterinary
Activities
The Abu Dhabi Municipality is responsible
for issuing health certificate for
licensing veterinary clinics and hospitals,
pharmacy license, health certificate
for pet trade license, trade cattle,
and sheep, and health certificate
for license slaughterhouse management.
ø Roads and Infrastructure
The Abu Dhabi municipality is responsible
for providing letter of no objection
for the establishment of a temporary
ramp, demolishing a building, constructing
a temporary fence, putting up the
crane, and for installing awnings
for cars.
ø Traffic Services
The Abu Dhabi Municipality is responsible
for traffic light signals and programs,
and traffic engineering studies.
ø Transportation and Loading
• The municipality is responsible
for permitting transfer of waste drilling
and the demolition of waste to designated
areas, permitting download of materials
from quarries.
• The municipality permits the
extension of services, including permit
for sidewalk upgrade, asphalt cutting,
bank guarantee release for workload
earthen quarry materials, spatial
data, map requests, maps based planning,
base maps, and maps satellite imagery.
• The municipality is responsible
for data requests, including data
based planning, data base maps, data
aerial photos, coordinating points
within the piece, and ground control
points.
• Public services, including
preview earth quarries, and delivery
to all corners of the earth, replacement
of documents, coordinating corners,
participating in the system network
stations cadastral (Surveying/Surveys
and maps).
• The municipality is responsible
for building permits, including licensing
of new apartment building on vacant
land, building new business license
on free land, licensing industrial
building new free land and new facilities
on vacant land, permitting new development
project establishment on free land,
and license procedure for adding a
building under construction. It also
permits the establishment of an amendment
to an existing building or an umbrella
within boundaries of the coupon, an
outer gate on the street, a makeshift
tent within or outside the boundaries
of the coupon, car garages outside
the boundaries of the coupon, installation
of tower crane, and retaining wall
drilling, and installation. It also
licenses an existing building, a fence
to an added land, development of deep
foundation, décor, comprehensive
building maintenance, work and settles
filling, and demolition of a building.
ø Architectural Credits
The municipality is responsible for
adopting architectural plans for the
construction of a new commercial,
residential, industrial, facility,
development, and structural system;
amendment to existing building, building
under construction; introducing in
addition to the existing building,
building under construction; and initial
development project.
ø Structural Funds
The municipality is responsible for
adopting structural plans for constructing
new residential, build a new business,
industry, facility, development; amendments
to existing building, building under
construction; introducing additional
building, building under construction,
and ad banners.
ø Inspection
The municipality is responsible for
inspection of foundation, temporary
fences, tiles, pickets, building completion,
and technical report regarding building
architect to the owner.
ø Public Services
The municipality is responsible for
temporary fence and building completion
certificates, contractor and consulting
firm registration or data modification,
and adoption of change and consulting
firm that oversees the construction
project.
ø Contractor Change
The municipality is responsible for
license renewal, cancelling building
permit request or building permit,
submitting a project plan for study
and accreditation, reporting of land
status, adopting matching architectural
plans for actual construction, extending
work hours at construction site, documents
or plans from archives, and gardens
and parks. The municipality also permits
service extension, green space removal,
a sub-point line that connects rainwater
drainage, pumping ground water, transmission
line irrigation or rainwater,
ø Violations and Fines
The municipality imposes fines on
detriment of green spaces due to construction
works. They also pay fines for damaging
the green spaces due to road accidents.
Other Activities
• Other activities of the municipality
include review and audit, and approval
of plans for new city designs, consulting
firm standard specification, notice
issuance to start work, requesting
material civilian approval, and releasing
security deposit for drainage work.
• Urban Planning: the municipality
adopts land sites, allocates residential,
commercial, industrial, farms land,
as well as land for development projects,
and break marine.
Impact of Abu Dhabi Municipality
on Abu Dhabi City
Abu Dhabi City and the associated
urban environments are increasingly
experiencing rapid growth illustrated
by increasing trade, population, traffic
movements, and vehicle ownership.
This section will discuss the positive
impact of Abu Dhabi Municipality on
Abu Dhabi City.
Environmental Safety and Awareness
Abu Dhabi Municipality is involved
in "Our Parks" campaign
to create awareness on recreational
facilities and public parks. The main
objective of the campaign is based
on the municipality's commitment and
social responsibility. The campaign
involves students from schools affiliated
to Abu Dhabi Education Council, and
park visitors. The campaign embodies
the strategy and mission of Abu Dhabi
Municipality that aim at enhancing
environmental awareness, and parks
and recreational facility appearance
as well as advancing the attitudes
and values that can conserve and protect
the components of the park from various
distortions. This campaign embeds
the spirit of social responsibility
among students so that they can protect
the parks and recreational facilities'
public properties, and informing them
of the best utilization of the venues
by refraining from making barbeques
except in designated places. In addition,
the ADM counsels the students on the
necessity to maintain park cleanliness
by ensuring that they drop trash in
designated containers, communicating
with visitors and students to acknowledge
the services and facilities required
in parks. They also diffuse environmental
culture and conserving parks through
establishment of workshops. The objective
of ADM is to ensure a smart civilized
appearance of Abu Dhabi City (Department
of Municipal Affairs, 2013).
The campaign is undertaken within
the framework of the objectives of
the municipality to promote community
outreach in preserving and protecting
recreational facilities and parks
with its community-based initiative
targeted at leveraging sports, recreational,
cultural, and environmental aspects
across the segments of the community.
It is a continuation of community
services management plan involving
community members with the municipality
to protect utilities, recreational
facilities, and installations, with
focus on public parks. It also reinforces
a culture of park frequenting due
to their positive bearing on urban
and modern appearance of the city
to increase environmental awareness
on the positive practices of maintaining
park cleanliness with their natural
elements and components, including
trees and plants. It also focuses
on educating park visitors on the
best way to dispose of barbeque remnants
and waste. These aspects include key
components of the environmental education
and awareness approach supported by
the Municipality of Abu Dhabi City
(Department of Municipal Affairs,
2013).
The Municipality has also organized
various workshops that aim at teaching
children the methods of growing plants
and flowers, and impart proper environmental
preservation practices among them.
The campaign also entailed workshops
on drawing and coloring and highlighted
certain elements that disturb public
gardens and parks. In addition, the
Municipality has plans of activating
educational and recreational programs,
associating the principles of communal,
familial, and individual responsibility
to protect urban facilities, maintain
gardens, and develop and utilize them
as places of natural and attractive
sites for other community-based programs.
These objectives are the foundation
upon with the Municipality of Abu
Dhabi strategy is built, that is,
to provide superior services based
on community involvement (Department
of Municipal Affairs, 2013).
Coordinating Infrastructure and
Construction Projects
The Abu Dhabi municipality has a huge
role in physical infrastructure in
Abu Dhabi City. However, this role
is associated with recurrent problems
of time and cost, which overrun their
development projects in the construction
industry (Benson, 2006). The delays
and cost overrun are also catastrophic
to the nation and the industry, and
may lead to unfavorable effects with
regard to national economic growth,
including holding back industrial
development and causing financial
losses (Halloum & Bajracharya,
2012; Odeh & Battaineh, 2002).
At micro level, cost overruns and
delays can result in arbitration,
dispute, total abandonment, and litigation
(Koushki, Al-Rashid & Kartam,
2005). In addition, it can lead to
contract termination, stressful acceleration,
and loss of productivity (Arditi &
Pattanakitchamroon, 2006).
Abu Dhabi Municipality is responsible
for infrastructure development in
Abu Dhabi City. It plays a major role
in the initiation of several projects
that are vital for development and
advancement of Abu Dhabi City. Some
of these projects include electricity
network, water supply and sewerage,
highway construction, and communication
cabling (Halloum & Bajracharya,
2012). However, Halloum and Bajracharya
(2012) through their review demonstrate
that improper assignment of roles
and responsibilities or inadequate
coordination among involved parties
can have negative impacts on the targeted
duration and cost of the project (EHSMS,
2009). Therefore, they suggest that
authorities need to insist on clarifying
the roles and distributing the responsibilities
of all parties clearly in the initial
project phases. In addition, there
is need for authorities to promote
proper sharing of knowledge among
stakeholders and appropriate coordination
among the parties involved. Consequently,
such measures are likely to reduce
the negative impacts associated with
the projects. The ADM should focus
not only on proper technical initiation
but also on ensuring continuity of
appropriate technical practices (Halloum
& Bajracharya, 2012).
Creation and Renewal of Urban Structures
Abu Dhabi Municipality also works
in collaboration with other partners
to create and renew urban structures,
including the development of Abu Dhabi
central market. They have worked in
conjunction with selected specialty
consultants to tackle the unique environmental
challenges and deliver construction
drawings in accordance with the aggressive
construction timetable to facilitate
infrastructural development (Halvorson,
Viise & Fenske, 2008).
Transportation Information Management
System (TIMS) and Road Safety
The Abu Dhabi Municipality roads directorate
acknowledges the need to develop well-structured
accident data gathering, management,
and analysis for the Abu Dhabi City
(Grosskopf et al., 2012). TIMS is
a key component of accident management.
The traffic police of the ADM is responsible
for accident recording, accident location
referencing, data/information exchange,
data storage, analysis, and reporting.
The accident information is useful
and can be used for enforcement, engineering,
and education. The ADM is responsible
for accurate collection and management
of accident data as a primary means
of improving road safety in Abu Dhabi
City (Khan, AlKathairi & Garib,
2011).
Demolition of Illegal Accommodation
The Abu Dhabi Municipality plays an
active role in the "clamp down
on illegal bachelor accommodation"
initiative. ADM is working in collaboration
with the police to enforce residential
laws, which restrict the number of
people to three people per room and
forbid makeshift partitions subdividing
rooms. The initiative was in response
to complaints from residents following
extensive investigation by the municipality.
Apart from involving inspectors in
checking for unlicensed additions
or partitions in villas, the initiative
also educates the public on environmental
and health risks associated with illegal
subdivisions of housing (Al Subaihi,
2013).
ADM also demolished abandoned or unoccupied
buildings, including commercial buildings,
villas, and government offices that
were undermining the beauty of Abu
Dhabi City or presented safety hazards.
Prior to the commencement of any demolitions,
the municipality conducts inventories
of disfigured or abandoned buildings,
commissions a consultant to prepare
a condition report prior to alerting
the owner of the building to demolish
the structure or carry out maintenance
works (National Staff, 2011). The
initiative aimed at relocation of
the bachelors to residential quarters
fitted with all means of security,
comfort, and suitable lodging provided
with all facilities, including transit
means, mosques, and shopping centres
to serve the Abu Dhabi City residents
(Al Subaihi, 2013).
Improving the Sustainability of
Low Income Housing Projects
The Abu Dhabi Municipality is increasingly
focusing on improving the sustainability
of low-income housing projects. They
have focused on ensuring a construction
process that is timely, cost effective,
of high quality, durable, cheaper
to maintain, user friendly, and with
good indoor environment (DSSCB, 2000).
They aim to achieve continued improvement
and annual reduction in the time and
cost of the project. Improving sustainability
of low-income buildings can be achieved
through assessment of the performance
of the buildings to identify any faults
or deficiencies and take measures
that enable the municipality to enhance
the performance of new projects in
Abu Dhabi City.
The municipality is involved in assessing
building performance in the City of
Abu Dhabi. Assessing and measuring
generally requires processes of checking
reviewing, monitoring, and evaluating
long-term and short-term the direction
and progress of departments, organizations,
projects, divisions, groups, functions,
and individuals. This ongoing process
aims at identifying the strengths,
and weaknesses of projects and strategies
for improvement. Consequently, corrective
measures are adopted to overcome the
weaknesses and improve performance
(Bassioni et al., 2004). Assessing
building performance has some benefits.
In the short-term, it allows for better
understanding of the performance and
functionality of the building and
comparing it against the stated criteria
during the design. They may also enable
the identification of problems before
improvement efforts are implemented.
In the mid-term, the use of data collected
in the assessment stage provides a
source of knowledge for planning of
new buildings that meet the city requirements.
In the long-term, it helps in the
establishment of databases, the generation
of planning, design criteria for specific
types of building, and enables the
designers to consider and document
their experience. This enables the
Abu Dhabi Municipality to avoid making
the same past mistakes as well as
acknowledge past success (Abdul-Rahman
et al., 2008). The accumulated information
is vital for enhancing the quality
of future buildings and services.
In addition, assessment results may
be used to improve design practice
by enlightening the designers that
there is a possibility of their buildings
being subject to scrutiny thereby
motivating them to maintain quality
and the performance of low-income
projects in Abu Dhabi City (Abdellatif
& Othman, 2006).
Agricultural Policies
The level of wastage of agricultural
produce in the Abu Dhabi Municipality
has reportedly been very high in the
previous years. However, the Municipality
has established agricultural policies
with an aim of improving the sector's
performance. Reports have shown that
the sector has experienced very rapid
developments resulting in increased
output over the years. The agricultural
policies set by the authorities have
been shown to be effective in encouraging
farmers to produce more through extensive
and intensive farming. However, the
marketing for vegetables and fruits
remains poor in Abu Dhabi. The policy
of the government on purchasing farmers'
products stimulates increased production,
but this has failed to match the level
and form of marketing of the farm
productions. The promotion of vegetable
and fruit labeling, packaging, and
presentation remains poor, the channels
of distribution remain poorly managed,
and the system of pricing does not
have a bearing on agricultural activity
cost structure or market competition.
Marketing research to understand the
market and the associated requirements
and build a marketing information
and database flow for marketing has
not been undertaken.
In the early 1990s, about fifty percent
of vegetables and fruits were reportedly
spoiled, dumped, and left over as
wastage. The major causes of wastage
were found to be lack of effective
presentation, marketing, and promotion
of vegetables and fruits, poor system
of distribution, lack of appropriate
training on packaging, handling, and
storage of vegetables and fruits,
and lack of import control and export
outlets, as well as uncontrolled government
policies, instruments, and incentives.
Based on these previous findings,
recommendations have been put across
so that the government can review
its incentive policies, especially
those related to training facilities,
purchase arrangements, pricing, and
support services (Tasha, 1994).
The Municipality has put in place
measures and awareness programs among
farmers to recycle farm waste annually
by turning it into compost fertilizers
to improve agriculture. There are
also plans to open up more markets
in residential areas to promote the
sale and purchase of fresh fruits
and vegetables within Abu Dhabi City.
The Abu Dhabi Municipality has also
put in place an initiative to increase
the marketing of locally produced
vegetables and fruits to increase
the market share of local products
in the city (Al Ali, 2013).
References
Abdellatif, M. A & Othman, A. E.
(2006). Improving the Sustainability
of Low-Income Housing Projects: The
Case of Residential Buildings in Musaffah
Commercial City, Abu Dhabi. Emirates
Journal for Engineering Research, 11(2),
47-58.
Abdul-Aziz Al Kindi. (2013). Process
of a new project.
Abdul-Rahman, H., Yahya, I., Berawi,
M., & Wah, L. (2008). Conceptual
delay mitigation model using a project
learning approach in practice. Construction
Management and Economics, 26, 15-27.
Abu Dhabi City Municipality. (2013).
Abu Dhabi Municipality. Retrieved from
http://www.adm.gov.ae/en/home/index.aspx.
Al Ali, K. A. (2013). The Economy -
Agriculture: 100 million Dirhams to
establish Agricultural Investment Fund.
Retrieved from http://www.uaeinteract.com/news/default3.asp?ID=18
Arditi, D. & Pattanakitchamroon,
T. (2006). Selecting a delay analysis
method in resolving construction claims.
International Journal of Project Management,
24(2), 145-55.
Al Subaihi, T. (2013). Abu Dhabi Municipality
to clamp down on illegal bachelor accommodation.
Retrieved from http://www.thenational.ae/abu-dhabi-municipality-to-
clamp-down-on-illegal-bachelor-accommodation>
Bassioni, H. A., Price, A.D.F. &
Hassan, T.M. (2004). Performance measurement
in construction firms. Journal of Management
in Engineering, 20(2), 42-50
Benson, R.W. (2006). Key issues for
the construction industry and the economy.
MidMarket Advantage, 16-18.
Department of Municipal Affairs. (2013).
Municipality of Abu Dhabi City embarks
on Phase III of "Our Parks"
<campaignhttp://adm.gov.ae/En/News/print.aspx?News_ID=676&MenuID=62&CatID=8
5&mnu=Cat&div=Cat> .
Department of Municipal Affairs. Abu
Dhabi Municipality (ADM) . Retrieved
16 December 2013 from www. ArabianBusiness.com.
DSSCB. (2000). Commercial Buildings
Directory: Department of Social Services
and Commercial Buildings. Abu Dhabi:
Al Wahdah-Express Printing Press.
EHSMS. (2009). Abu Dhabi Environment,
Health and Safety Management System
Regulatory Framework (EHSMS), 1-25.
Retrieved on 16 December, 2013, from
https://www.ead.ae/_data/global/EHSMS%20Updated/AD%20EHSMS%20Guideline%
20- %20Entity%20Guideline%20to%20Assist%20with%20Development%20of%20EHSMS.
pdf
Grosskopf, S., Kazemi, T., Hughes, J.,
Almusawi, S., & Hashim, B. (2012).
Road Safety Assessment and Road Safety
Audits on the Existing Abu Dhabi International
Road Newtwork. Conference Proceedings
(pp. 573-583). Abu Dhabi: Adventure
Works Press.
Halloum, M. A. & Bajracharya, A.
(2012). Cost and Time Overrun Revisited:
A Study on the Infrastructure Construction
Projects in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Advancing
Civil, Architectural and Construction
Engineering & Management, 4-6.
Halvorson, R., Viise, J. & Fenske,
E. (2008). Abu Dhabi Central Market
Redevelopment. Creating and Renewing
Urban Structures, 1-8.
Khan, M. A., AlKathairi, A. S. &
Garib, A. M. (2011). A. GIS base traffic
accident data collection, referencing
and analysis framework for Abu Dhabi,
1-11.
Koushki, P.A., Al-Rashid, K. & Kartam,
N. (2005). Delays and cost increases
in the construction of private residential
projects in Kuwait. Construction Management
and Economics, 23(3), 285-294.
National Staff. (2011). Hundreds of
buildings demolished by Abu Dhabi Municipality
http://www.thenational.ae/news/uae-news/200-abu-dhabi-buildings-demolished-since-
2011
Odeh, A. M. & Battaineh, H. T. (2002).
Causes of construction delay: traditional
contracts. International Journal of
Project Management, 20(1), 67-73.
Rafi. (2013). Responsibilities &
Roles of Abu Dhabi Municipality. Abu
Dhabi Municipality.
Tasha, A. N. A. (1994). Developing a
Strategy for Increasing the Efficiency
of the Marketing of Selected Agricultural
Produce in the United Arab Emirates.
Master's thesis, Middlesex University
|