|
The Effect of Job Rotation on employees
in organizations in the UAE

Sasha Hodgson (1)
Maleeha Al Shehhi (2)
Eman Al-Marzouqi (2)
(1) Dr. Sasha
Hodgson, Assistant Professor
Zayed University, Abu Dhabi, United
Arab Emirates
(2) Graduate student, Zayed University,
Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Correspondence:
Dr. Sasha Hodgson, Assistant Professor
Zayed University,
P.O. Box 144534
Abu Dhabi
United Arab Emirates
Email: Sasha.Hodgson@zu.ac.ae

Abstract
Job rotation is a type of on-the-job
knowledge acquiring where an employee
is encouraged through a list of coursework
planned to give them an extent of
practical knowledge and coverage of
different aspects of employment for
that profession. Job rotation is a
suitable
development method for employees who
are focusing only on common job tasks
rather than a specialized professional
route. It is also a way of obtaining
speedy coverage and experience to
a large selection of positions within
a company in order to boost certain
capabilities. The basic purpose of
this study is to find out the impact
of job rotation on employees in UAE
public and private (both) organizations.
For this purpose, online survey technique
was used and data was gathered from
100 employees including males and
females from UAE organizations. Data
was analyzed through reliability,
descriptive, correlation and regression
analysis. The findings of the study
show that job rotation has a highly
significant and positive impact on
employees in both the public and private
sector in United Arab Emirates organizations.
Job rotation creates new opportunities
for employees and develops high skills
in them.

Introduction
Nowadays, "upgrading the knowledge
and capabilities of personnel, equipping
employees with the most up-to-date
and unique capabilities, improving
upon productiveness and worth-extra
operations, blocking personnel skills
from turning into obsolete and enhancing
the coaching lifestyle." (Ortega,
2001). "Job rotation is a serious
component of work layout and an industrial
observe normally used along with the
intention of lowering monotony and
building substantial inspiration."
(Huang, 1999)
According to Jorgensen (2005) "Rotation
is usually described as performing
at different tasks or in numerous
positions for established intervals
of time."
"In the planned way applying
lateral transfers aiming to permit
employees to gain a range of information,
skills and competencies and can be
noticed being an on-the-work training
technique." (Gomez and Lorente,
2004). Therefore, it is thought to
gain an effect on worker determination.
"Job rotation is a part of job
system where the employees transfer
from one position to another in a
specific period of time to do different
tasks compared to the previous positions.
It can be defined as working in different
positions and doing different tasks
for a period of time in an organization
in order to learn a different range
of skills and knowledge." (Jorgensen
et al, 2005). Also, according to Eriksson
& Ortega (2006) "Job rotation
is an effective way to develop employees'
abilities". This research has
been investigated in UAE organizations
of how employees can benefit from
job rotation. It could check with
different types of rotations.
Job rotation certainly is a kind
of on-the-career knowledge enhancing
wherever an employee moves through
a timetable of assignments intended
to provide them with several career
experiences. "Task rotations
are appropriate progress remedies
for employees who are in search of
a general instead of technical job
path, need to reach quick exposure
to wide range of employment in an
organization, or need to have to reinforce
particular skills. Position rotations
can be obtained for workers at all
grades and levels within the organization,
nonetheless are almost certainly to
be useful for fresh new graduates
or higher opportunity leaders."
(Huang, 1999).
"In the United States of America
they applied job rotation throughout
the nineteenth century which was a
regular exercise during the Business
of labor in a very prominent American
spiritual communal motion called the
United Modern society of Believers,
normally known as the Shakers, as
discovered by the diaries and journals
of many Shaker members." (Andrews,
1963). "In US firms, skilled
employees who are predicted to be
promoted as professionals are needed
to use a broad perspective of your
complete business. The personnel have
seasoned many manufacturing segments
by rotating through distinctive work
opportunities, properly learning quite
a few aspects of the company from
the supervisor point of view."
(Brewer, 1986).
Yet, job rotation in Japan is totally
different from other countries as
well as the UAE. For example, "the
Japanese-style (is) shuffling the
Japanese workers into new disciplines
every few years. So, it is not necessary
for them to specialize in specific
areas because they know that Japanese
companies implement frequent job rotation
which is a practice that is rare in
Western corporations. Also, it often
occurs in large Japanese companies
in order to give the company vitality
and unity." (Lohr, 1982).
On the other hand, the UAE government
started to plan and apply job rotation
in 2012. This was suggested and agreed
by H.E. Humaid Mohammed Al Qatami,
Chairman of the Federal Authority
for Government Human Resources (2012)
"We seek to put an end to the
culture of staying in the same post
for a long time as rotating jobs allows
the leading posts to be continuously
provided with qualified national staff."
This idea was followed according to
UAE Federal Government Learning and
Development Policy v1.0 -Article 62
(n.d) "Job rotations are available
to employees at all grades and levels
within the organization, however are
most likely to be used for fresh graduates
or high potential leaders."(P,
17)
Implementing job rotation has different
impacts on employees. "Job rotation
is an effective way to develop employees'
abilities and they need to gain deeper
understanding of more aspects of business."
(Eriksson & Ortega, 2006)
Moreover, "job rotation is a
suitable development solution for
employees who are seeking a general
rather than technical career path
and who need to gain rapid exposure
to a wide range of jobs within an
organization (e.g. new employees or
fresh graduates.)" (UAE Federal
Government Learning and Development
Policy, n.d). Besides, "job rotation
would provide working environment
flexibility to employees in order
to exert their multi skilling in the
working process" (Armache, 2012).
Furthermore, as job rotation becomes
an essential part of the workplace
we are estimating that UAE organizations
after 10 years would hugely increase
the process of job rotation in different
sectors (public and private) due to
the optimistic effects on employees
that would encourage them to reach
a high standard level of knowledge
where the productivity and motivation
would raise in this case. It's beneficial
for us to do this research to evaluate
the effects of job rotation on employees
who are currently working in UAE organizations.
Hypothesis
For our research we would like to
investigate the following hypotheses
related to job rotation in the UAE
which are:
H1a: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employees
of the UAE public and private sector.
H1b: There is a negative relationship
between job rotation and employees
of the UAE public private sector.
H2: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
social relationship of the UAE private
and public sector.
H3: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
knowledge and skills of the UAE private
and public sector.
H4: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
routine work of the UAE private and
public sector.
H5: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
job opportunity of the UAE private
and public sector.
H6: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
performance level of the UAE private
and public sector.
H7: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
job stress of the UAE private and
public sector.
We have chosen this topic because
we want to find out the impact of
job rotation on employees in UAE organizations.
The basic purpose of choosing these
hypotheses is to provide evidence
of how job rotation can prove progression
and enhancement alternatives for UAE
Federal Government workforce in addition
to comparing the public and the private
sectors, to be certain that Government
has the capability to meet their future
prerequisites in each technical and
management role. As a result, it would
help to emphasise the top quality
in scheduling and controlling as well
as discovering and progress activities
at all stages in each private and
non-private sector of United Arab
Emirates organizations.
In this research, we estimate that
job rotation may positively affect
employees more who are in UAE private
sector rather than who job rotated
in the public sector. This estimation
was built on the International Journal
of Human Resource Management, where
a Human Resource manager stated that
"Employees are more attracted
to private sector offers of career
development and learning opportunities."
(Al-Hamadi et al, 2007). This means
that the career development is a part
of developing more skills which will
be applied through job rotation.
In this case, we will evaluate our
hypotheses by comparing the responses
of each employee, for different gender,
in the private sector and public sector
in UAE, which depends on the employee's
gender, age, skills enhancement, improving
social relationships and which sector
they work in, and are they satisfied
with job rotation application or are
they stressful about this process.
Therefore, we will be able to classify
their opinions for both sectors.
Methodology
In this particular study, we have
chosen online survey approach as a
primary method to gather our data.
The basic purpose and advantages of
choosing online survey method are:
• Low costs. "Resulting
from greatly lower overheads, collecting
knowledge does not have to cost you
in a large number." (Evan &
Mathur, 2005).
• Automation and real-time
access. "Respondents enter
their own individual data, and it
is really immediately saved electronically.
Analysis, results therefore in being
easier and will be streamlined, and
is available straight away."
(Evans & Mathur, 2005)
• Less time. "Fast
deployment and returning of questionnaire
are feasible with online surveys that
can't be attained by traditional procedures.
If you have negative contact information
and facts for some respondents, you
will realize it virtually appropriate
once you have dispatched your surveys."
(Evans & Mathur, 2005)
• Convenience for respondents.
"They might respond to questions
on their agenda, at their speed, and
may even begin a study at a single
time, postponed, and finish it later
on." (Evans & Mathur, 2005)
• Design flexibility.
"Surveys can be programmed even
when they are quite elaborate. Intricate
skip styles and logic might be utilized
seamlessly. You can even require that
respondents offer just one response
to solitary-alternative thoughts,
which cuts down on error." (Evans
& Mathur, 2005)
In order to measure the statement
given by respondents in the survey,
a 5 point Likert scale was used:
1. Strongly disagree
2. Disagree
3. Neutral
4. Agree
5. Strongly Agree
In this way, we can identify the responses
of each employee who works in the
Private and Public sector, linked
with the effects of job rotation system.
Population
The desired and actual population
for this particular study is all employees
who practice job rotation in their
departments of public and private
sector of United Arab Emirates organizations.
Sample Size
The sample size for this particular
study is 100 employees including males
and females. The sample size has been
chosen through simple random sampling.
In statistics, a simple random sample
is a subset of people taken from a
bigger population. Just about every
individual is decided on randomly
and entirely based on random selection,
so that each person has the exact
probability of remaining preferred
at any phase through the sampling
system, and every subset of k men
and women has the same likelihood
of remaining picked out for sample
as every other subset of k individuals.
"This process and procedure is
named simple random sampling. A simple
random sample is undoubtedly an unbiased
surveying method." (Yates et
al, 2008).
Data analysis
To see the relationship between independent
and dependent variables, the sample
was employed as well as correlation
and multiple regressions. The data
was analyzed for the descriptive portion
related to job rotation effects. The
first step required the application
of correlation model development of
social relationship, increased knowledge
and skills, decreased routine work,
decreased stress, increased job opportunity,
improved performance level and employees'
job satisfaction. This meant that
there were six independent variables.
All of them had the multiple regression
model applied to them.
Y= b0
+b1X1+
b2X2+
b3X3+
b4X4+
b5X5+
b6X6+e
Y=
employee's job performance/satisfaction
(dependent variable)
b0=
Constant
X1= Build social
relationship
X2= Broaden
job knowledge and skills
X3= Decreased
routine work
X4= Decreased
stress
X5= Increased
job opportunity
X6= Improved
performance level
With the help of the above given
equation, the effects of independent
variables on the dependent variable
of job employees' satisfaction/performance
were measured.
Findings of
the study
Reliability for both sectors (Public
and private)
Table 1
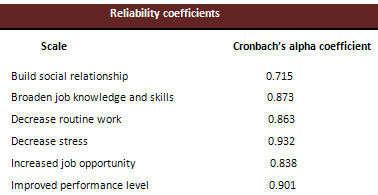
Table 1 shows
that instrument used in this study
was reliable with Cronbach's alpha
value of 1st independent variable
(Build social relationship) 0.715,
with Cronbach's alpha value of 2nd
independent variable (broaden job
knowledge and skills) 0.873, with
Cronbach's alpha value of 3rd independent
variable (decreased routine work)
0.863, with Cronbach's alpha value
of 4th independent variable (decreased
stress) 0.932, with Cronbach's alpha
value of 5th independent variable
(increased job opportunity) 0.838
and with Cronbach's alpha value of
6th independent variable (improved
performance level) 0.901.
Descriptive statistics for (Private
sector )
Table 2
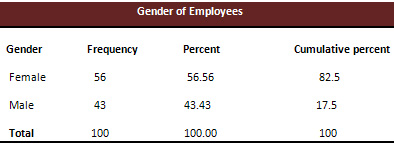
Table 3
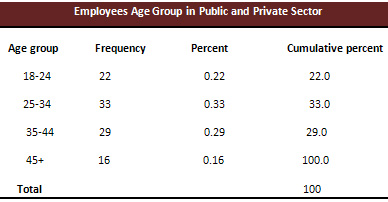
Table 2 & Table 3 show that there
were 56.56% males and 43.43% females
participated in the particular study.
Out of them, 22% respondents were
of 18-24 age groups. 33% respondents
were of 25-34 age group, 29% respondents
were of 35-44 age group and 16% respondents
were of 45+ age group.
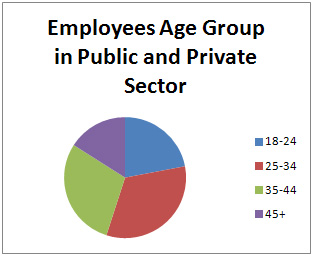
Table 4
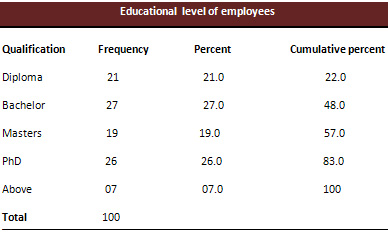
Table 5
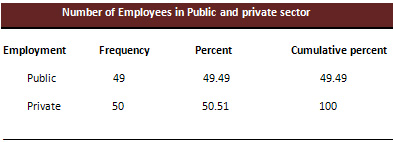
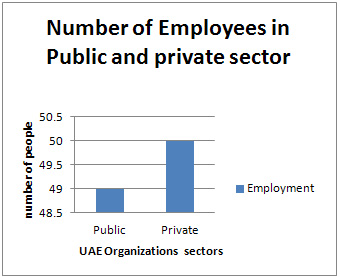
Table 6
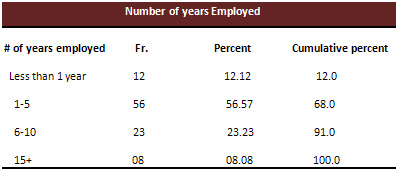
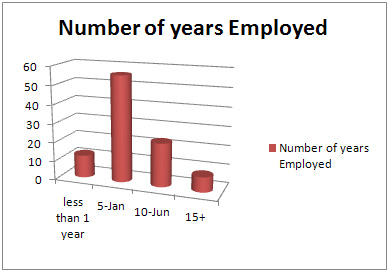
Table 7
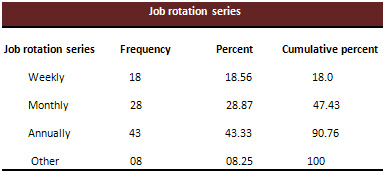
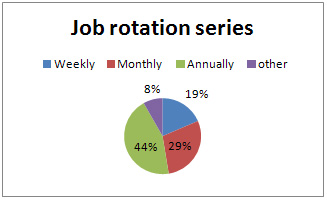
Correlation
Table 8
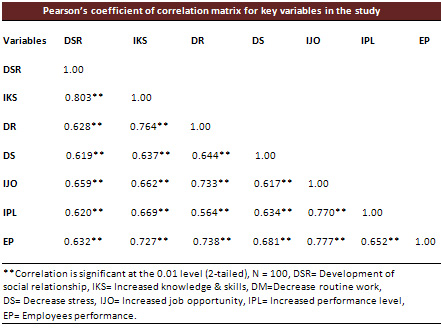
Table 8 shows that association between
all variables is positive. Significant
relationship is also found among many
variables. Employee's performance/satisfaction
has a positive and strong correlation
with all variables at 0.01 significant
levels. All independent variables
are highly significant and positively
correlated with each other at 0.01
significant levels.
Regression
Regression table measures the amount
of total variation in dependent variable
due to independent variable. Table
9 shows the value of Adjusted R2 is
0.922. This value indicates that there
is almost 73.4% variation in dependent
variable (employee's performance/satisfaction)
due to one unit change in independent
variables. The F value is 85.525 at
0.000 significant levels, which shows
that the model is good as its value
is less than 0.01 significant levels.
Table 9
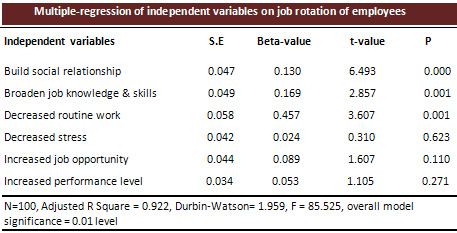
Table 9 shows that with a significant
level of 0.000 and t value 6.493 build
social relationship (the beta value
of independent variable) is 0.130.
Similarly, the increased job knowledge
& skills (beta value of independent
variable) is 0.169 with significant
variable and t value of 0.001 and
2.857 respectively. For decreased
routine work (the beta value of independent
variable), the beta value is 0.457
with 0.001 significant level and 3.607
t value. These values illustrate how
much the dependent variables such
as employees' performance/satisfaction,
are being affected by independent
variables.
Results
The results of this study show that
job rotation has a significant effect
on employee's performance/satisfaction
in UAE organizations and all the dimensions
that were taken to measure job rotation
are showing significant and positive
results with employees except "decreased
stress". It is very obvious that
any new job or task that is known
to an employee can give him/her stress,
for that reason moving between job
tasks should have a proper time length
where the employees of private and
public sector have time to adapt to
that change and start feeling comfortable.
The rest of all the dimensions, including
development of social relationship,
decreased routine, increased job performance,
increased knowledge & skills and
increased job opportunity are highly
positively related to employees. On
the basis of these results, we can
say that some of our hypotheses are
being accepted which are:
H1a: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employees
of the UAE public and private sector.
accepted
H2: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
social relationship of the UAE private
and public sector. accepted
H3: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
knowledge and skills of the UAE private
and public sector. accepted
H4: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
routine work of the UAE private and
public sector. accepted
H5: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
job opportunity of the UAE private
and public sector. accepted
H6: There is a positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
performance level of the UAE private
and public sector. accepted
However, two of our hypothesis had
an opposite results which are:
H1b: There is a negative relationship
between job rotation and employees
of the UAE public private sector.
H7: There is positive relationship
between job rotation and employee's
job stress of the UAE private and
public sector.
Conclusion
The research was about evaluating
the effect of job rotation on employees
in organizations in the UAE. Where
this process has great positive effects
on employees depends on their career
and how they act toward the rotation
technique. We measured different factors
that may enhance employees' job accomplishment
while job rotating. Finally, job rotation
can serve both employees and their
organization goals where they will
be able to create optimistic productiveness
to reach high standard levels since
they have an employee who is featured
with multiple experiences and skills.
References
Al-Hamadi, A., Budhwar, P., and Shipton,
H. (2007). Management of Human Resource
in Oman. International Journal of
Human Resource Management, 18(1),
100-113.
Andrews, E. D. (1963). The People
Called Shakers. Dover Publications:
New York.
Armache, J. (2012). Effect of compensation
and other motivational techniques
on organizational productivity. Franklin
Business & Law Journal, (1), 88-96.
Retrieved May 16, 2014,from http://web.ebscohost.com/ehost/detail?sid=0f5b0792-bed7-46cd-b1f7
a226662b839a%40sessionmgr110&vid=1&hid=113&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#d
b=bth&AN=75144022
Brewer, P. J. (1986). Shaker Communities,
Shaker Lives, University Press of
New England: Hanover.
Eriksson, T and J. Ortega (2006) .The
Adoption of Job Rotation: Testing
the Theories, Industrial and Labor.
Relations Review, Vol. 59, 653-666.
Evans, J and Mathur, A (2005). "The
value of online surveys". Internet
Research, Vol. 15 Issue: 2, pp.195
- 219
Gomez, P. J., Lorente, J. J. C. &
Cabrera, R. V. (2004). Training practices
and organizational learning capability
relationships and implications. Journal
of European Industrial Training, 28(4),
234-256.
Huang, H. J. (1999). Job rotation
from the employees point of view.
Human Resource Management, 7(1), 75-85.
Jorgensen, M. (2005). Characteristics
of job rotation in the midwest US
manufacturing sector. Ergonomics,
48(15), 1721-1733.
Lohr, S. (1982). HOW JOB ROTATION
WORKS FOR JAPANESE. The New York Times.
Retrieved May 25, 2014, from http://www.nytimes.com/1982/07/12/business/how-job-rotation-works-for-japanese.html
Ortega, J. (2001): Job Rotation as
a Learning Mechanism. Management Science,
Vol. 47, 1361-1370.
Qatami, M. A. (2012). Share this item
Al Qatami at the 1st Leaders Program
Forum: The Government Adopts Job Rotation.
FAHR Event. Retrieved May 27, 2014,
from http://www.fahr.gov.ae/Portal/en/news/1/10/2012/
UAE Federal Government Learning and
Development Policy (n.d.). Training
& Development System for Federal
Government. The Federal Government
Human Resources. Retrieved May 18,
2014, from http://www.fahr.gov.ae/Portal/Userfiles/Assets/Documents/7d6edd9.pdf
Yates, Daniel S.; David S. Moore,
Daren S. Starnes (2008). The Practice
of Statistics, 3rd Ed. Freeman. ISBN
978-0-7167-7309-2.
|